Vegan vs. Vegetarian: What is the difference between vegan and vegetarian? We unravel the differences so you can better understand the distinctions between these diets and lifestyles!

With the popularity of plant-based diets increasing every year, more people are embracing their potential benefits for health, the environment, and animal welfare.
As we explore these dietary choices, it’s helpful to recognize the distinctions between vegan and vegetarian diets to make informed decisions about our food choices.
What is Vegan?
A vegan diet is a strict form of plant-based eating, excluding all animal products and by-products, such as meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, and honey. Some products, such as refined sugars and gelatins, are excluded due to the use of animal products during processing.
Vegans rely on plant-based foods, including fruits, vegetables, grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds, to meet their nutritional needs.
Common motivations for adopting a vegan lifestyle include ethical concerns about animal welfare, a desire to reduce environmental impact, and the pursuit of health benefits associated with a plant-based diet.
What is Vegetarian?
A vegetarian diet is a less restrictive form of plant-based eating, excluding meat, poultry, and fish, while allowing for the consumption of some animal-derived products.
Like vegans, vegetarians often adopt this lifestyle due to ethical concerns, environmental sustainability, and health benefits.

What is the Difference Between Vegans and Vegetarians?
Vegans exclude all animal-derived products, while vegetarians consume some, such as dairy and eggs.
Ethical considerations may be more stringent for vegans, who avoid all forms of animal exploitation as they consider them all equal.
Both diets can reduce environmental impact, but a vegan diet may have a lower footprint due to the complete exclusion of animal products.
Both diets can offer health benefits, such as lower risk of chronic diseases, but a vegan diet may provide additional advantages due to the complete elimination of animal products.
Vegan vs. Vegetarian
Now that you know the basic differences between vegans and vegetarians, let’s get into the fine details about the different types of vegans and vegetarians. There is a variety of differences within each of these diets and lifestyles.
Types of Vegans
There are six different types of vegans, each having its own reasons for following this diet or lifestyle. Here we break down the types of vegans – ethical, environmental, health-focused, raw, whole food plant-based, and junk food vegans.
Ethical Vegans
Ethical vegans adopt a vegan lifestyle primarily due to concerns about animal welfare and rights. These individuals not only avoid consuming animal products but also reject the use of products derived from animals or tested on animals, such as leather, fur, and cosmetics.
Environmental Vegans
Environmental vegans choose a plant-based diet to reduce their environmental impact, as animal agriculture contributes significantly to greenhouse gas emissions, deforestation, water pollution, and other environmental issues. These vegans often adopt sustainable practices in other aspects of their lives as well.
Health-Focused Vegans
Health-focused vegans adopt a vegan diet primarily for health reasons, such as reducing the risk of chronic diseases, improving weight management, and promoting overall well-being. They may be more focused on consuming whole, plant-based foods and avoiding processed vegan alternatives.
Raw Vegans
Raw vegans follow a diet consisting of uncooked and unprocessed plant-based foods. They typically consume fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, and sprouted grains, and avoid cooking their food above a certain temperature (usually around 118°F or 48°C) to preserve the natural enzymes and nutrients.
Whole Foods Plant-Based Vegans
Whole-food plant-based vegans emphasize consuming whole, minimally processed plant-based foods, such as fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds. They avoid processed vegan alternatives, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats to maximize the health benefits of their diet.
Junk Food Vegans
Junk food vegans primarily consume processed and convenience foods that are vegan but may not necessarily be healthy. Their diet can include items like vegan fast food, snacks, desserts, and processed meat and dairy substitutes. While this type of veganism aligns with the ethical and environmental aspects of the lifestyle, it may not offer the same health benefits as other types of vegan diets.
Types of vegetarians
As with vegans, there are different types of vegetarian diets. Each with different reasons behind their diet or lifestyle. We’ll break down the differences between – lacto, ovo, lacto-ovo, pescatarian, and flexitarian vegetarian diets.
Lacto-vegetarian
Lacto-vegetarians include dairy products, such as milk, cheese, and yogurt, in their diets but exclude eggs, meat, poultry, and fish.
Ovo-vegetarian
Ovo-vegetarians consume eggs but do not eat dairy products, meat, poultry, or fish.
Lacto-ovo vegetarian
Lacto-ovo vegetarians are the most common type of vegetarian diet, which includes both dairy products and eggs in their diets but excludes meat, poultry, and fish.
Pescatarian
Pescatarians, while not strictly vegetarian, abstain from eating meat and poultry but include fish and other seafood in their diets. Some pescatarians may also consume dairy and eggs.
Flexitarian or Semi-vegetarian
Flexitarians follow a primarily plant-based diet but occasionally consume meat, poultry, or fish in small quantities. This type of diet is more flexible and may be adopted as a stepping stone toward a more restrictive vegetarian or vegan lifestyle.
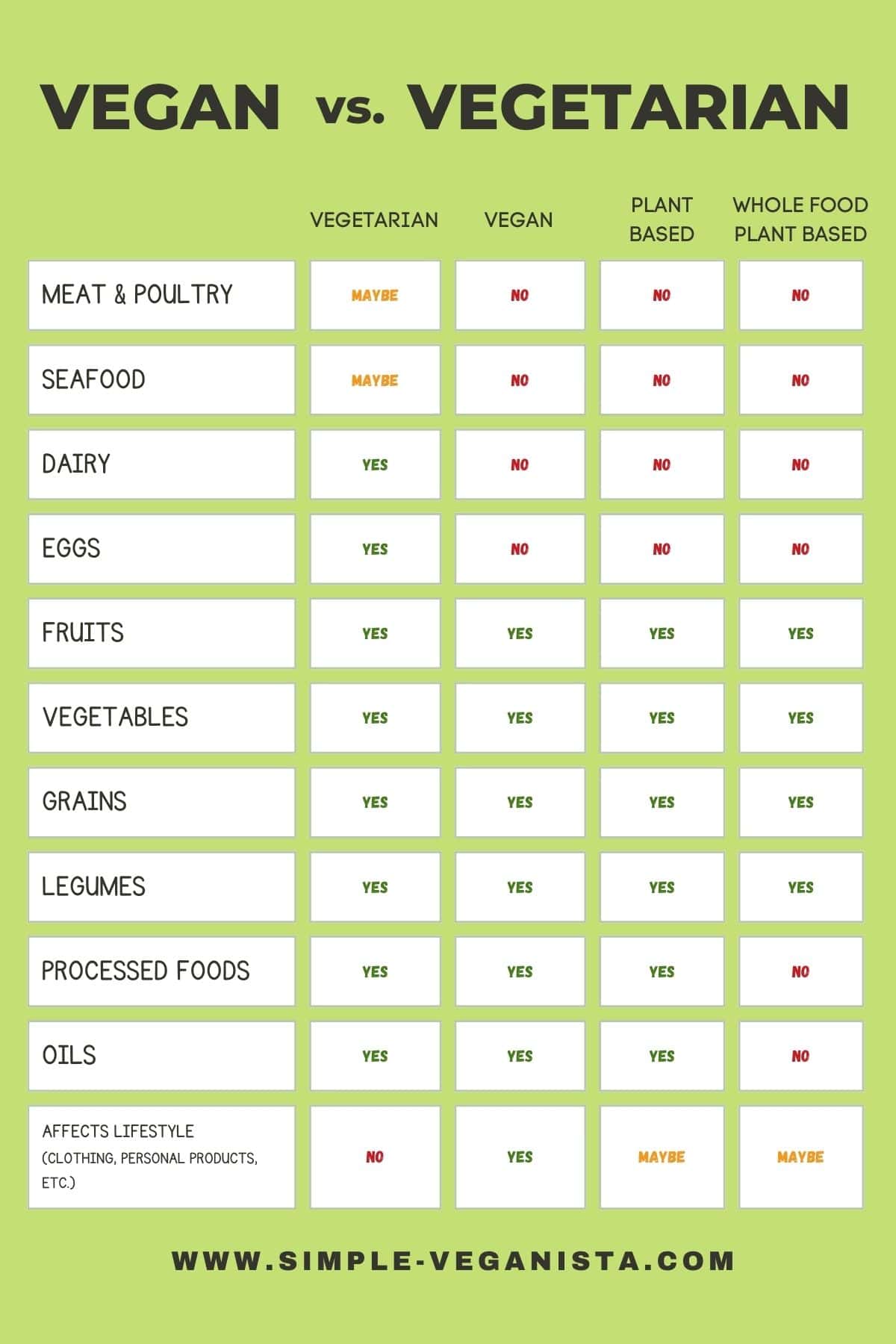
🌱 Vegan vs. Vegetarian Food Chart
Here’s a look at the generalized differences between vegan vs. vegetarian vs. plant-based food choices and whether the diet also affects other personal lifestyle choices.
Considering a vegan or plant-based diet? Be sure to take a look at our Beginner’s Guide to a Plant-Based Diet to get you started!
Nutritional Considerations for Vegans and Vegetarians
Both diets require attention to ensure adequate intake of essential nutrients, such as iron, vitamin B12, calcium, and omega-3 fatty acids.
A well-planned vegan or vegetarian diet can meet all nutritional needs, but it’s important to include a variety of plant-based foods and, when necessary, consider supplementation.
Recommendations for supplementation may vary between the two diets, with vegans requiring more attention to nutrients like vitamin B12, which is primarily found in animal products.
🌱 Read more about vegan and vegetarian sources of Vitamin B12, Calcium, Iron, Vitamin D, and Omega-3.


FAQ’s
No, while both vegan and vegetarian diets focus on plant-based foods and share some common motivations, such as health, animal welfare, and environmental sustainability, they are not the same. Vegetarians consume animal products, while veganism involves a more comprehensive approach, encompassing both dietary and lifestyle choices that aim to eliminate the use of animal products entirely.
Eggs are considered vegetarian but not vegan. This is because eggs come from chickens, quail, or other farm egg-laying animals, and vegans do not consume any type of animal product.
Cheese is considered vegetarian, unless it is cheese made from plant-based ingredients. Always look at the packaging and labels to notice the difference between traditional dairy cheese and plant-based cheese.
Yes, vegan food is suitable for vegetarians. A vegan diet is a stricter form of plant-based eating that excludes all animal products and by-products, including meat, poultry, fish, dairy, eggs, and honey. Since vegetarian diets also exclude meat, poultry, and fish, they share some commonalities with a vegan diet. With a well-planned vegan diet, vegetarians can get all the nutrients they need. Also, it’s always a good idea to speak to your medical provider, as dietary needs can differ. Visit our Beginner’s Guide to a Plant-Based Diet to get started.
Lacto-vegetarian: Lacto-vegetarians include dairy products, such as milk, cheese, and yogurt, in their diets but exclude eggs, meat, poultry, and fish.
Ovo-vegetarian: Ovo-vegetarians consume eggs but do not eat dairy products, meat, poultry, or fish.
Lacto-ovo vegetarian: The most common type of vegetarian diet, lacto-ovo vegetarians include both dairy products and eggs in their diets but exclude meat, poultry, and fish.
Pescatarian: While not strictly vegetarian, pescatarians abstain from eating meat and poultry but include fish and other seafood in their diets. Some pescatarians may also consume dairy and eggs.
Flexitarian or Semi-vegetarian: Flexitarians follow a primarily plant-based diet but occasionally consume meat, poultry, or fish in small quantities.
Ethical Vegans: A vegan lifestyle that not only avoids consuming animal products but also reject the use of products derived from animals or tested on animals, such as leather, fur, and cosmetics.
Health-focused Vegans: A vegan diet is adopted primarily for health reasons, such as reducing the risk of chronic diseases, improving weight management, and promoting overall well-being.
Raw Vegans: Raw vegans follow a diet consisting of uncooked and unprocessed plant-based foods.
Whole Foods Plant-Based Vegans: A vegan diet that emphasizes eating whole, minimally processed plant-based foods and avoiding processed vegan alternatives, refined sugars, and unhealthy fats.
Junk Food Vegans: A vegan diet that primarily consumes processed and convenience vegan foods that are vegan but may not be healthy.
Food For Thought
Recognizing the unique aspects of vegan and vegetarian diets helps us appreciate the choices individuals make based on their values, beliefs, and health goals.
By understanding the differences between these plant-based lifestyles, we can make more informed decisions about our food choices and support others on their journey towards a healthier, more sustainable way of living.
Both vegan and vegetarian diets have the potential to offer numerous benefits, and embracing a plant-based lifestyle can be a powerful way to improve our health, protect the environment, and promote compassion for all living beings.

